Technical indicators in Forex are essential tools for traders, designed to facilitate market analysis and inform trading decisions. They help traders identify trends, find the best entry and exit points, and evaluate market volatility.
Many indicators, such as moving averages, RSI, and Bollinger Bands, generate clear trading signals that help access trends accurately. Furthermore, these indicators enhance understanding of the current market conditions and assist in forecasting future price movements.
In this article, we will explore top Forex indicators that can be used in various trading strategies.
The article covers the following subjects:
Major Takeaways
- Technical indicators in Forex help traders analyze the market, identify price trends, and find entry points.
- MACD, RSI, and Bollinger Bands are key analysis tools.
- Some indicators, like the Ichimoku Cloud, show trends and support levels.
- ATR and ADR measure volatility and help set trading targets.
- Fibonacci levels and the Parabolic SAR are used to spot reversals.
- Momentum indicators, ADX, and Aroon focus on trends.
- Combining indicators in your trading system improves analysis accuracy and reduces risks.
- The choice of indicators depends on the trading style and goals of a forex trader.
What Are Technical Indicators?
Technical indicators are tools that help traders analyze the Forex market and predict price movements. They are based on mathematical calculations using data such as prices, volumes, and time. Indicators process chart information and present it in a way that helps traders understand market trends.
Technical indicators are usually divided into two types: leading and lagging. Leading indicators, like the stochastic oscillator, generate signals before price movements start. Lagging indicators, such as moving averages, confirm trends after they are already established. For example, the RSI shows if an asset is overbought, while Bollinger Bands are a volatility indicator.
Different indicators serve various purposes, such as identifying trends, finding entry/exit points, measuring volatility, and analyzing volume. Using indicators allows traders to create more precise trading strategies and reduce risks. These technical tools are available on MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader, and the LiteFinance online terminal.
How to Сhoose the Best Forex Indicators?
It is important to consider your strategy and goals when selecting an indicator. Trend-following indicators, such as MACD, Ichimoku Cloud, and ADX, help identify the direction of price movement. Market volatility can be assessed using ATR and Bollinger Bands. If you’re seeking indicators for overbought and oversold levels, the RSI and Stochastic Oscillator are excellent choices. Fibonacci levels and Parabolic SAR are instrumental in identifying reversal points.
Combining indicators allows you to improve analysis accuracy. For example, using RSI with MACD helps confirm signals for opening and closing positions. The right tools depend on your experience, the market, and the timeframe.
MACD Indicator
The MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) is a popular indicator used to analyze the strength, direction, and duration of a trend. It consists of two moving averages (fast and slow) and a histogram showing the difference between them.
MACD line crossovers signal potential shifts in market sentiment, while the histogram highlights trend strength.
To apply the indicator, look for crossovers of the MACD lines with the signal line. When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it suggests that upward momentum is increasing, signaling a potential buy opportunity. When the MACD line crosses below the signal line, it indicates growing downward momentum, signaling a potential sell opportunity.
Use this indicator with other tools, such as RSI or Bollinger Bands, to improve forecast accuracy.
RSI Indicator
RSI (Relative Strength Index) is an indicator used in technical analysis. It measures the strength and speed of price changes, indicating overbought and oversold levels. RSI values range from 0 to 100, where levels above 70 indicate overbought conditions, and levels below 30 indicate oversold conditions.
To apply RSI, use those levels to enter and exit trades. For example, a buy position can be opened when the RSI reaches the 30 level, while a sell position can be opened after it reaches the 70 level. The indicator also helps identify divergences, signaling potential trend reversals.
To improve accuracy, combine RSI with trend indicators, such as MACD or Bollinger Bands.
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are used to assess market volatility and identify potential support and resistance levels. The indicator consists of three lines: a moving average and two standard deviations above and below.
When the price approaches the upper band, the market is likely overbought, while touching the lower band indicates oversold conditions. Narrowing bands indicate low volatility and a possible strong momentum. Bollinger Bands help find entry and exit points, especially when combined with RSI or MACD to confirm signals.
Ichimoku cloud
The Ichimoku Cloud is a versatile indicator that shows trends, support and resistance levels, and potential reversal points. The Ichimoku Cloud consists of five components: two key levels (Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen), the cloud formed by Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B, and Chikou Span (Lagging Span).
When the price is above the cloud, the market is bullish; when below, it indicates a bearish trend. Crossovers of the Tenkan-sen and Kijun-sen lines generate buy or sell signals. The cloud highlights consolidation zones and helps forecast future price movements. Use the Ichimoku Cloud for comprehensive analysis by combining it with other tools, such as RSI or volume indicators.
Exponential Moving Average
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a popular technical indicator that places greater emphasis on recent prices than the Simple Moving Average (SMA). This makes the EMA more responsive to price changes and quicker to react to market movements.
The EMA is used to determine the direction of a trend and identify entry and exit points.
When the price is above the EMA, the trend is upward; when below, the trend is downward. Crossovers of the EMA with the price or other moving averages signal potential reversals. The EMA is often combined with indicators like MACD and RSI to refine signals.
Alligator Indicator
The Alligator Indicator (developed by Bill Williams) is a tool for identifying trends and their phases. It consists of three moving averages: the jaw (blue line), teeth (red line), and lips (green line), shifted by a specific number of periods.
When the lines diverge, the indicator signals the start of a trend (the Alligator is “awake”). If the lines intertwine, the market is in a consolidation phase (the Alligator is “sleeping”). Use the Alligator to identify trends and pinpoint entry points. For optimal results, combine it with other indicators.
On Balance Volume
The OBV (On-Balance Volume) indicator analyzes trading volume to predict price movements. It measures volume accumulation and distribution: if the price closes higher than the previous close, the volume is added; if lower, it is subtracted.
OBV helps detect divergences between volume and price. If OBV rises while the price remains stable, the price will likely increase. If OBV decreases while the price rises, a reversal is possible. This indicator is used to confirm trends and signals from other tools, such as the moving average indicator or MACD.
Stochastic Oscillator
The Stochastic Oscillator is a momentum indicator that identifies overbought and oversold conditions in the market. It compares the current closing price to the price range over a specific period and ranges between 0 and 100.
Levels above 80 indicate overbought conditions, while levels below 20 suggest oversold conditions. Crossovers of the %K and %D lines generate buy or sell signals. For instance, a crossover from below to above signals a buy opportunity. The oscillator performs best in flat markets and is often combined with RSI or MACD.
Fibonacci retracement
Fibonacci retracement levels are based on mathematical ratios. This tool helps identify potential support and resistance levels where the price may retrace before continuing the trend.
Key levels include: 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, 78.6%, and 100%. The levels are drawn based on price extremes. Traders use them to find entry and exit points. For example, if the price pulls back to the 61.8% level and starts rising, it may signal a buying opportunity. Fibonacci levels are especially effective when combined with other indicators, such as MACD and moving averages.
Average Directional Index (ADX)
The Average Directional Index (ADX) is one of the top forex indicators that measures the strength of a market trend, regardless of its direction. The indicator values range from 0 to 100: readings above 25 indicate a strong trend, while a value below 20 suggests a weak or sideways market.
The Average Directional Index (ADX) consists of three lines: the ADX itself, which measures the trend’s strength, and two Directional Indicators (+DI and -DI) that indicate the direction of the trend. Crossovers of the +DI and -DI lines help determine whether buyers or sellers dominate. Traders use ADX to filter signals from other indicators to avoid trading during weak trends.
Parabolic Stop and Reverse (SAR)
The Parabolic SAR (Stop and Reverse) is a trend indicator used to determine entry and exit points. It is displayed as dots above or below the candles on a chart.
When the dots are below the price, the trend is upward, signaling a buy opportunity. If the dots are above the price, the trend is downward, signaling a sell. The SAR works well in trending markets but may produce false signals during consolidation. It is often used alongside other technical tools for confirmation.
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is one of the best forex indicators that measures market volatility. It shows how much the current price deviates from the average price. A high standard deviation indicates increased volatility.
This indicator is useful for assessing risk: an increase in deviation may signal the start of a strong trend, while a decrease suggests consolidation. It is often used with Bollinger Bands, which are based on standard deviation. Traders apply it to identify entry and exit points, especially in trending markets.
ATR indicator
The Average True Range (ATR) indicator measures market volatility.
It shows the average range of price movement over a specific period. ATR does not indicate the trend direction but helps assess risk and set stop-loss levels.
When ATR values rise, volatility increases, which may signal strong price movements. A lower ATR suggests market stability. A high ATR means a wider stop-loss range is needed. ATR works well with trend indicators like EMA or MACD.
CCI (Commodity Channel Index)
The Commodity Channel Index (CCI) is an oscillator that measures how far the current price is from its average over a set period. Values above +100 indicate overbought conditions, while values below -100 suggest oversold conditions.
Traders use CCI to find entry and exit points for trades. For example, the CCI line crossing above -100 can signal the potential beginning of a bullish trend. Conversely, crossing below +100 may indicate that upward momentum is weakening, which could signal a potential selling opportunity. CCI also helps detect divergences that point to possible trend reversals.
Pivot Point
A Pivot Point is a chart indicator used to identify key support and resistance levels. It is calculated based on previous price highs, lows, and closing prices.
The Pivot Point acts as a central level around which the price may fluctuate. If the price is above the Pivot Point, the market is considered bullish; if below, bearish. Traders use additional levels (S1, S2, R1, R2) to determine entry and exit points.
Pivot Points are commonly used in intraday trading to identify critical price levels.
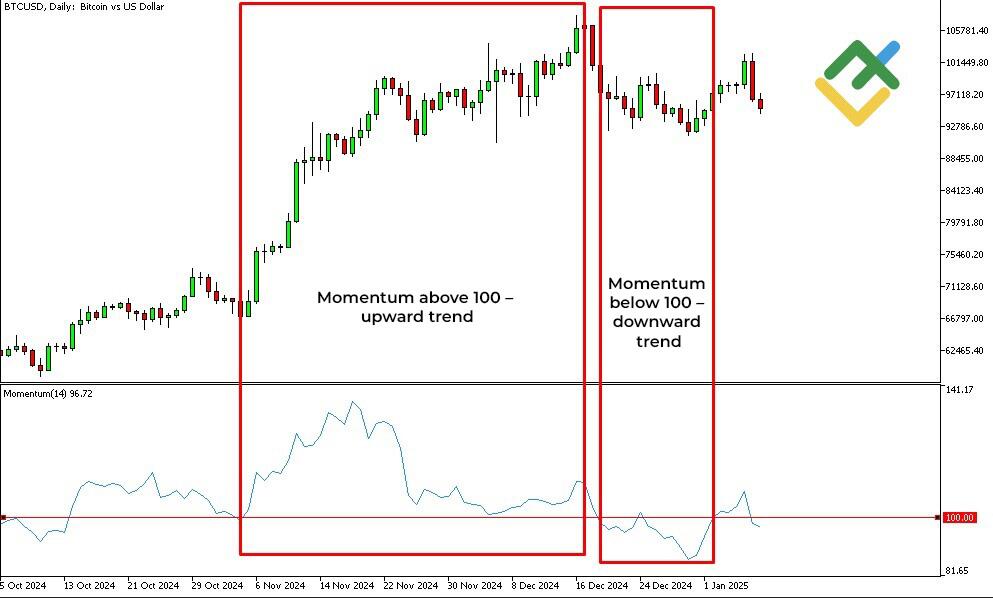
Momentum Indicator
The Momentum indicator measures the speed of price changes over a specific period, helping to assess trend strength. It is displayed as a line comparing the current price to the price N periods ago.
Rising momentum signals a strengthening trend, while falling momentum indicates weakening. Values above 100 confirm a bullish trend, while values below 100 confirm a bearish trend. Traders use momentum to find entry and exit points and detect divergences. The indicator is effective when combined with RSI or MACD.
Aroon indicator
The Aroon indicator identifies the trend direction and its strength. It consists of two lines: Aroon-Up shows the number of periods since the last high, and Aroon-Down shows the number of periods since the last low.
When Aroon-Up is above 70, it indicates a strong uptrend. When Aroon-Down is above 70, it suggests bearish momentum or the possibility of a downtrend. The crossing of the lines may signal a trend reversal. This indicator is used to detect the beginning and end of trends and works well with other tools to confirm signals.
Average Daily Range (ADR)
The Average Daily Range (ADR) measures the average price movement range over a specific number of days. It helps traders assess market volatility and set realistic trade targets.
ADR is used to estimate the price movement potential within a day. For example, if the price approaches the maximum ADR range, further movement becomes less likely. The indicator is instrumental in determining entry and exit points, especially in intraday trading. It is often combined with tools like moving averages and Pivot Points.
Conclusion
Technical indicators for MT4 and MT5 are essential tools for Forex trading. Leading indicators, such as the Stochastic Oscillator, help identify potential market changes in advance and provide signals before price movements occur. Lagging indicators, like Moving Averages, confirm already established trends, enabling more informed trading decisions. Multi-purpose technical Indicators, including RSI and Bollinger Bands, help analyze market volatility and identify overbought or oversold conditions.
Use indicators to enhance accuracy of analysis, reduce risks, and make more balanced trading decisions.
Learn to use technical tools on LiteFinance’s demo account and try building a reliable trading strategy with them.
Get access to a demo account on an easy-to-use Forex platform without registration
Frequently Asked Questions About Forex Technical Indicators
The choice of indicators depends on the trader’s goals. MACD is suitable for trend identification, Bollinger Bands for volatility, and RSI for spotting overbought/oversold conditions. Combining indicators can improve analysis accuracy.
Indicators help analyze the market, find entry and exit points, identify trends, and assess volatility. Their effectiveness depends on understanding how they work and using them correctly alongside other analysis tools.
Accuracy depends on market conditions. Moving Averages work well in trending markets, RSI is effective in flat markets, while Bollinger Bands perform well during high volatility.
The best fundamental indicators for Forex trading are economic data such as unemployment reports, GDP, and interest rates. These reflect overall economic trends affecting currency pairs.
The best approach is a combination of technical and fundamental analysis. Technical analysis using indicators helps identify entry and exit points, while fundamental analysis evaluates overall market trends and key economic events.
The profitability of an indicator depends on the strategy. For example, RSI is effective in flat markets, while moving averages are better for trending markets. Combining indicators enhances signal accuracy and potential profitability.
Most traders use indicators such as Bollinger Bands, RSI, and moving averages to analyze trends, identify overbought or oversold conditions, and support informed trading decisions effectively.
Moving averages and ADX are the most effective for confirming trends. Moving averages show the price direction, helping traders spot long-term trends. ADX measures trend strength, confirming its sustainability and filtering out false signals.
The content of this article reflects the author’s opinion and does not necessarily reflect the official position of LiteFinance. The material published on this page is provided for informational purposes only and should not be considered as the provision of investment advice for the purposes of Directive 2004/39/EC.
{{value}} ( {{count}} {{title}} )
This post is originally published on LITEFINANCE.