When trading Forex, traders often consider whether to use a market or limit order. The only difference is that a market order allows you to execute trades immediately, while a limit order enables you to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price and time. Besides, a limit order provides a more precise entry into the market, whereas a market order enables swift reactions to market volatility. As a result, each order is good in its way. Let us analyze which one is better — a market or limit order.
The article covers the following subjects:
Key Takeaways
-
A market order is an order to buy or sell an asset at the current market price.
-
A limit order is an order to buy or sell an asset in the future at a predetermined price set by the trader. If the market reaches that price, the order will be executed.
-
A market order allows you to react instantly to rapid price changes and open a trade immediately but requires constant monitoring of the situation. The specific market entry price depends on the broker and market volatility.
-
A limit order helps open a position without the trader’s direct involvement, guaranteeing the best execution price regardless of volatility. It is only triggered when the conditions set by a trader are met.
-
When you place a market order, you can only set stop-loss and take-profit levels after opening a position. However, you can place take-profit and stop-loss orders simultaneously with a limit order.
Get access to a demo account on an easy-to-use Forex platform without registration
What is the Limit Order?
While trading stocks or currencies, a trader may realize that a trend will reverse soon. In this case, a regular market order will not help. Instead, we can use a limit order to open a trade in the future at a predetermined price.
A limit order is a special market order to buy or sell an asset in the future at a predetermined level. In other words, a sell or buy order is set anywhere on the price chart. When the price reaches this level, it triggers the order, and a trade is opened.
A limit order is designed to execute a transaction according to the parameters set by a trader in advance. When the price reaches the set limit level, it triggers a limit order, which initiates a buy or sell position, depending on the order type.
In other words, assuming that the EURUSD pair will hit its bullish price target of 1.1000 and reverse to the downside, you can set a sell limit order at this level. If the price reaches 1.1000, a short trade will be opened. A buy limit order works the same way.
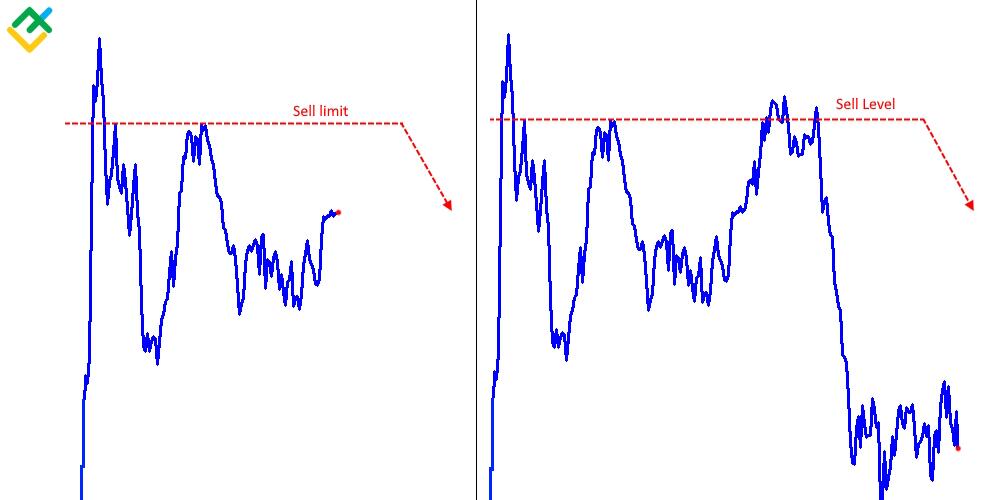
Limit Order Example
Let us look at the sell limit order on the price chart of a currency pair.
Since the limit order is set in advance, the left chart shows that the current price is below the sell limit order level. The idea behind this order is that we do not know when the price will climb to the order level, but we expect it to reach it.
Setting a limit order is quite simple and involves several steps. First, you should determine whether it is a buy or sell operation. It is seen that the price will grow slightly and reverse downwards. The reversal and the price drop are particularly important. If you are going to profit from the price decline, a sell order should be set. Then, determine at what point it is better to sell or find the level at which the order or the selling price will be set. Optionally, you can set stop-loss and take-profit orders to fully automate the process.
After some time, the price triggered the order. Then, the asset reversed and started to fall. The idea has been realized, and the trade now brings profit.
Limit Order Pros and Cons
The most well-known advantage of limit orders is trading automation, but these orders also have disadvantages.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
What is the Market Order?
A market order is the simplest and most basic operation in financial market trading. It is used to buy or sell an asset. In fact, a market order is a transaction or an instruction to a broker to buy or sell an asset.
A market order is a basic order to buy or sell an asset at the current market price. In other words, you give an order to a broker to sell or buy an asset at the current market price, and the order is executed immediately. After that, you can take profits or suffer losses, depending on the type of order — buy or sell.
Assuming that the EURUSD price will rise to 1.1000 now or soon, you should open a buy position at the current market price. When the asset reaches 1.1000, you will have a floating profit on your account, which can be taken by closing the trade. The same is true for a sell order.
Market Order Example
Let us analyze the sell and buy orders on the price chart.
The chart shows that sell and buy market orders are at the same level as the current price. Market orders are useful for quick trades or when you do not have a specific plan.
Setting a market order is simple. First, decide whether you want to buy or sell. When buying or selling an asset, the price is expected to move in the desired direction immediately. If the price is about to fall, one should sell. If it is expected to rise — buy.
Let’s set two buy and sell orders at the same point. This will clearly demonstrate how market orders work. Whichever way the price moves, one order will make a profit while the other will result in a loss. The outcome can be seen after some time.
As you can see, the price has fallen. This means that a sell position is profitable, and a buy one makes a loss. A net profit would be made if only a sell order had been set.
Market Order Pros and Cons
A market order is the most basic and simplest type of order. Although it is considered the most efficient one, it also has a number of disadvantages.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
Key Differences
Market and limit orders are undoubtedly very similar. However, you need to choose the right trading strategy to fully experience their advantages.
The main differences between these orders when trading on the live market are listed below:
-
Trade execution time. Limit orders are used to set the price at which the order will be automatically executed without the direct involvement of a trader. With market orders, you instruct the broker to open a trade at the current market price.
-
Execution probability. A market order will always be executed because it is an instruction. This means the broker will execute a trade at the price closest to the current market price, regardless of how far it is from your desired price. A limit order is an intention. It indicates to the broker that you want to buy or sell at a specific price. However, if this price is not available in the market, the order will not be executed.
- Use in strategies. Market orders are good when dealing with fundamentals. When an expected event occurs, you want to make a trade immediately rather than wait for an asset to hit a predetermined price. Limit orders are designed for technical analysis strategies. Most automated trading systems are based on them. Limit orders are also good for trading with patterns. Besides, limit orders can become an efficient supplement to your trading strategy, especially if it involves chart patterns. Notably, patterns can help determine the trigger price but cannot tell when the asset price will hit it.
Market Order vs. Limit Order Comparison Table
It may be helpful to compare limit and market orders in a table that assesses their application in trading to understand their differences better.
|
Limit order |
Market order |
|
|
Purpose |
Limit orders are used to open transactions in the future at a specific market price |
Market orders are meant to execute trades immediately at the current market price |
|
Trading types |
Is used to follow the current trend and trade at trend reversal |
Is set according to a trend |
|
Execution method |
Executed when the market price reaches the order trigger level |
Executed immediately at the current market price |
|
Duration |
Limit orders often include the expiration date or time. If the order has not been filled by that date, it is deleted |
Market orders are expiration-free, as they are almost always executed immediately |
Start trading with a trustworthy broker
Conclusion
Although limit orders offer precise settings and guarantee the best execution price, market orders are more commonly used in transactions. Market orders are especially popular with private traders seeking immediate results.
In general, the type of order used to open a trade does not really matter as long as it is profitable. The order type only affects how the trade is carried out, but the result does not depend on it. Profitability is determined by choosing the right entry point into the market. When the profit is taken, it is not important whether you used a limit or market order.
FAQs on Limit vs Market Order
The main advantage of a limit order is its execution at a precisely set price. If a trader has specified the desired execution price and it is available in the market, the order is guaranteed to be executed at this price. Market orders are filled at the nearest price in the depth of market, which may not be the price you want.
Limit orders include stop, limit, and stop-limit orders. Stop orders are sell stop and buy stop. Limit orders are divided into sell limit and buy limit. Stop-limit orders include sell stop-limit and buy stop-limit.
The main disadvantage of a limit order is that it does not guarantee execution. A limit order is filled only if the limit price coincides with the market price. If they don’t match, the order will not be executed.
Yes, a limit order can fail to be executed in two cases. First, the order may not be filled if the asset has not reached the desired limit price. Second, the order may fail if the market price slips through the limit order level, which may happen during price gaps.
The content of this article reflects the author’s opinion and does not necessarily reflect the official position of LiteFinance. The material published on this page is provided for informational purposes only and should not be considered as the provision of investment advice for the purposes of Directive 2004/39/EC.
{{value}} ( {{count}} {{title}} )
This post is originally published on LITEFINANCE.